Internal 아키텍처 개요
목표
- Internal 아키텍처의 레이어와 그 역할을 이해합니다.
- 아키텍처 트릴레마(캡슐화, 순수성, 성능) 관점에서 각 설계 요소의 필요성과 트레이드 오프를 확인합니다.
주요 키워드
- Internal 아키텍처 & External 아키텍처
- 관심사의 분리
- 레이어
- 순수 & 불순 함수
아키텍처 정의
아키텍처 분류

- External 아키텍처: 프로세스 외부, 서비스 배치
- Internal 아키텍처: 프로세스 내부, 레이어 배치
아키텍처 원칙
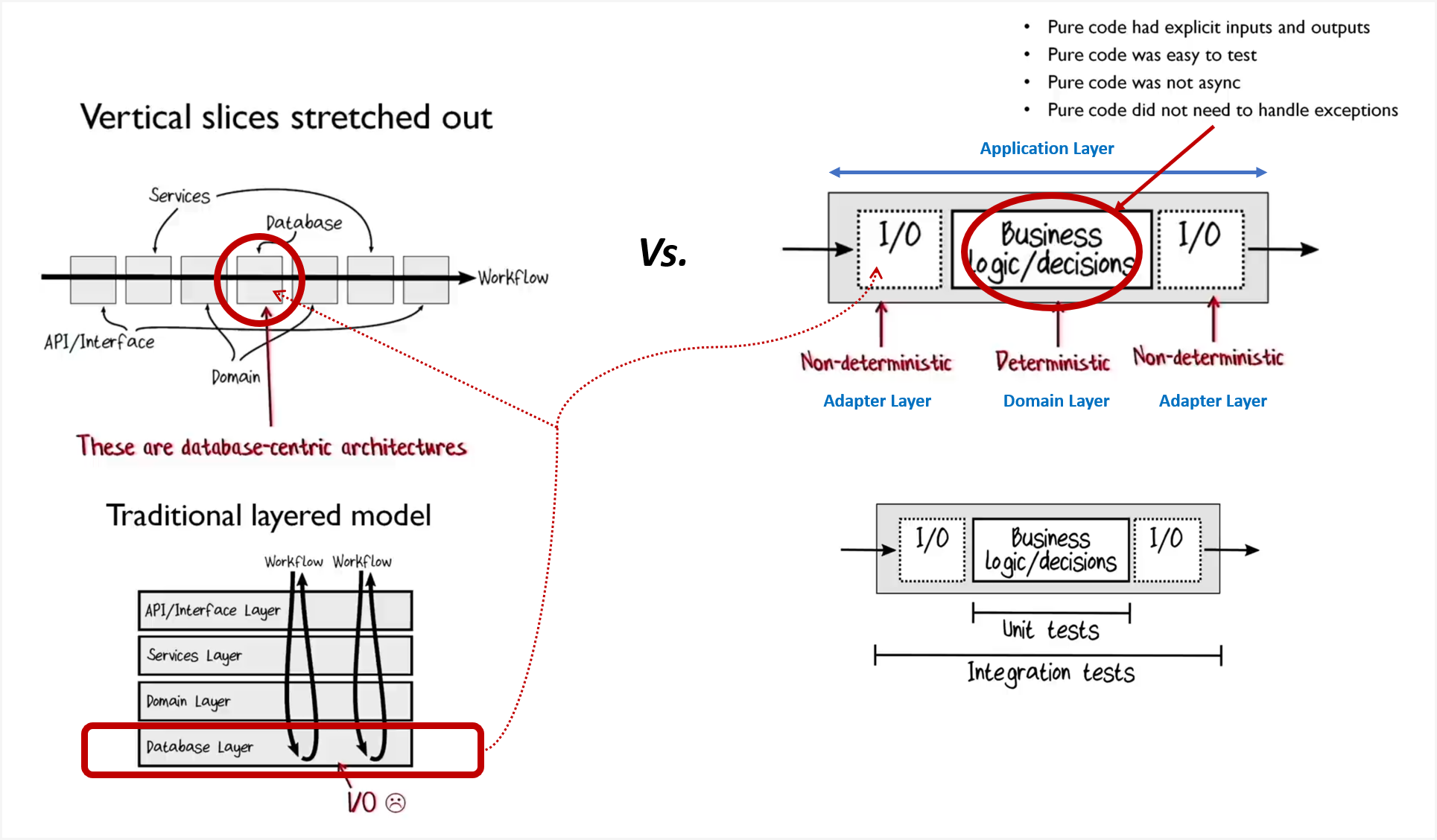
- 관심사의 분리(Separation of concerns): 기술과 비즈니스를 분리한다.
- 결정을 내리는 코드: 비즈니스(순수 함수: 숨은 입출력이 없는 함수)
- 해당 결정에 따라 작용하는 코드: 기술(불순 함수: 숨은 입출력이 있는 함수)
- 관심사는 레이어로 관리합니다.
- 비즈니스 레이어
- 비즈니스 단위: Domain
- 비즈니스 흐름: Application
- 기술 레이어: Adapter
- 비즈니스 레이어
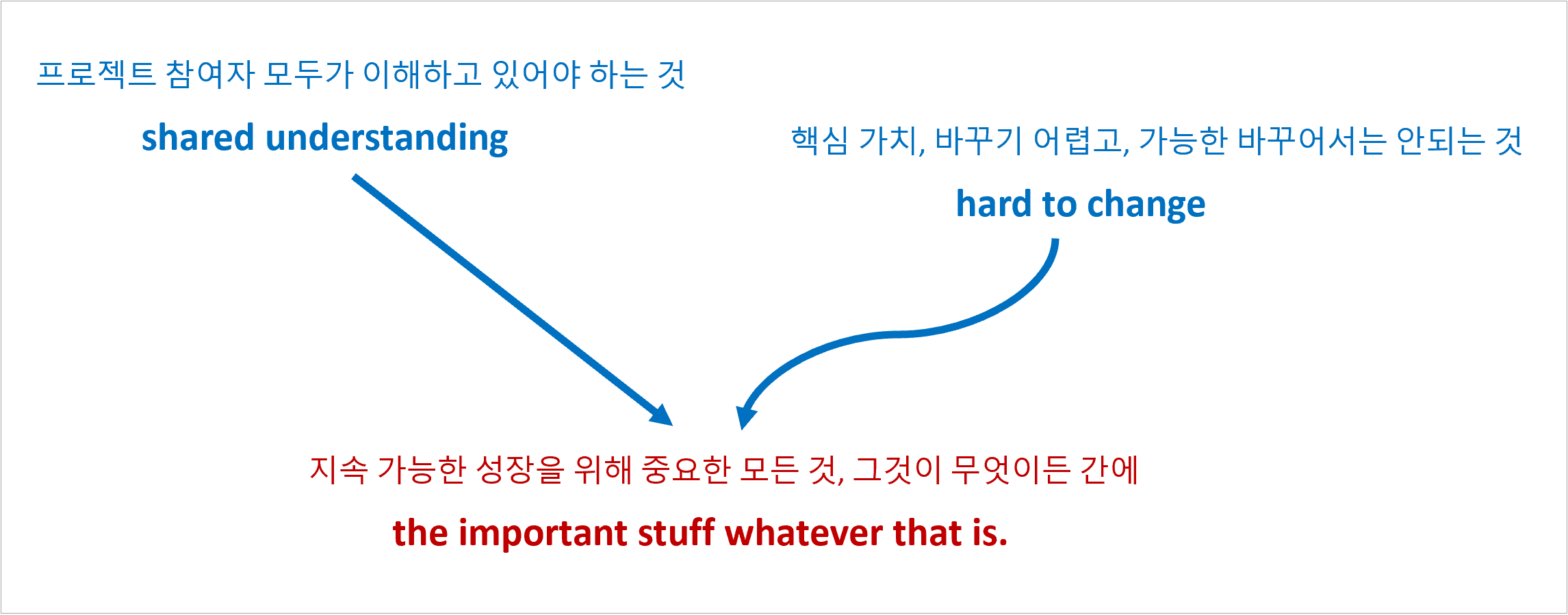
아키텍처 트릴레마(trilemma)
세 가지 선택지나 목표 중에서 오직 두 가지만 만족할 수 있고, 나머지 하나는 포기해야 하는 상황을 가리킵니다.
즉, 세 가지 조건이나 목표를 동시에 달성할 수 없는 딜레마의 확장판이라 볼 수 있습니다.
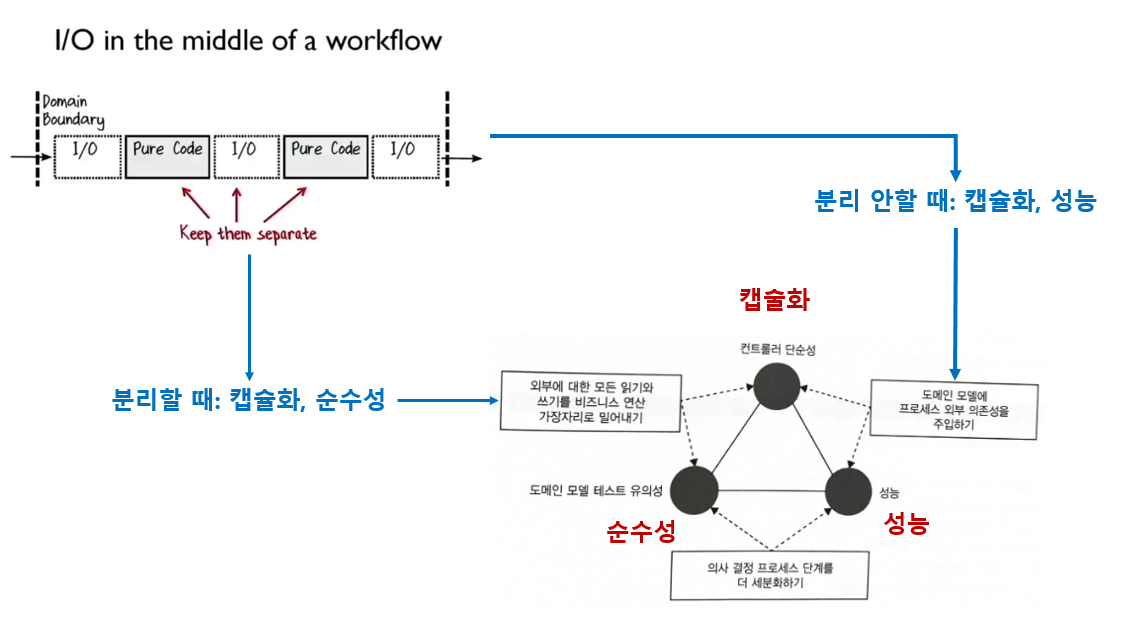
예제 코드 1.

- “결정을 내리는 코드”와 “해당 결정에 따라 적용하는 코드”을 분리합니다.
- 순수 함수: 결정을 내리는 코드
- 불순 함수: 해당 결정에 따라 적용하는 코드
예제 코드 2.
cs
public class AuditManager
{
private readonly int _maxEntriesPerFile;
private readonly string _directoryName;
public AuditManager(int maxEntriesPerFile, string directoryName)
{
_maxEntriesPerFile = maxEntriesPerFile;
_directoryName = directoryName;
}
public void AddRecord(string visitorName, DateTime timeOfVisit)
{
string[] filePaths = Directory.GetFiles(_directoryName);
(int index, string path)[] sorted = SortByIndex(filePaths);
string newRecord = visitorName + ';' + timeOfVisit.ToString("s");
if (sorted.Length == 0)
{
string newFile = Path.Combine(_directoryName, "audit_1.txt");
// 메서드 시그니처에 정의 안된 숨겨진 출력: 숨겨진 의존성
File.WriteAllText(newFile, newRecord);
return;
}
(int currentFileIndex, string currentFilePath) = sorted.Last();
List<string> lines = File.ReadAllLines(currentFilePath).ToList();
if (lines.Count < _maxEntriesPerFile)
{
lines.Add(newRecord);
string newContent = string.Join("\r\n", lines);
// 메서드 시그니처에 정의 안된 숨겨진 출력: 숨겨진 의존성
File.WriteAllText(currentFilePath, newContent);
}
else
{
int newIndex = currentFileIndex + 1;
string newName = $"audit_{newIndex}.txt";
string newFile = Path.Combine(_directoryName, newName);
// 메서드 시그니처에 정의 안된 숨겨진 출력: 숨겨진 의존성
File.WriteAllText(newFile, newRecord);
}
}솔루션 구성
| Level | Src | Tests |
|---|---|---|
T1 | Corporation | Corporation |
T2 | Solution | Solution |
T3 | Service 또는 UI | Service 또는 UI |
T4 | Layers | Tests |
T5 | Sub-Layers | Test Pyramid |
- Layers
T4DomainT4ApplicationT4: AdaptersT5InfrastructureT5PersistenceT5Presentation
- Test Pyramid
T4TestsT5UnitT5IntegrationT5PerformanceT5E2E(End to End)
{T2}.sln
│ # 자산(Assets) 범주: Backend와 Frontend을 구성하기 위해 자산 코드
├─Assets
│ ├─Frameworks
│ │ ├─Src
│ │ │ ├─{T1}.{T2}.Framework
│ │ │ └─{T1}.{T2}.Framework.Contracts
│ │ └─Tests
│ │ └─{T1}.{T2}.Framework.Tests.Unit
│ ├─Libraries
│ │ ├─{T1}.{T2}.[Tech] // 예. RabbitMQ, ...
│ │ └─...
│ └─Domains
│ ├─Src
│ │ └─{T1}.{T2}.Domain
│ └─Tests
│ └─{T1}.{T2}.Domain.Tests.Unit // 공유 도메인
│
│ # Backend 범주
├─Backend
│ ├─{T3}
│ │ ├─Src
│ │ │ ├─{T1}.{T2}.{T3} // Host 프로젝트
│ │ │ ├─{T1}.{T2}.{T3}.Adapters.Infrastructure // Adapter 레이어
│ │ │ ├─{T1}.{T2}.{T3}.Adapters.Persistence // Adapter 레이어
│ │ │ ├─{T1}.{T2}.{T3}.Application // Application 레이어
│ │ │ └─{T1}.{T2}.{T3}.Domain // Domain 레이어
│ │ └─Tests
│ │ ├─{T1}.{T2}.{T3}.Tests.Integration // Integration 테스트
│ │ ├─{T1}.{T2}.{T3}.Tests.Performance // Performance 테스트
│ │ └─{T1}.{T2}.{T3}.Tests.Unit // Unit Test
│ ├─{T3}
│ │ ├─Src
│ │ └─Tests
│ └─Tests
│ └─{T1}.{T2}.Tests.E2E // End to End 테스트
│
│ # Frontend 범주
└─Frontend
└─{T3}
├─Src
│ ├─{T1}.{T2}.{T3} // Host 프로젝트
│ ├─{T1}.{T2}.{T3}.Adapters.Infrastructure // Adapter 레이어
│ ├─{T1}.{T2}.{T3}.Adapters.Persistence // Adapter 레이어
│ ├─{T1}.{T2}.{T3}.Application // Application 레이어
│ └─{T1}.{T2}.{T3}.Domain // Domain 레이어
└─Tests
├─{T1}.{T2}.{T3}.Tests.Integration // Integration 테스트
├─{T1}.{T2}.{T3}.Tests.Performance // Performance 테스트
└─{T1}.{T2}.{T3}.Tests.Unit // Unit Testpowershell
.\new-sln -t1 Corp -t2 Hello -t3s Master, ApiT1: CorporationT2: SolutionT3:T3S: Backend ServiceT3U: Frontend UI
프로젝트 의존성 다이어그램
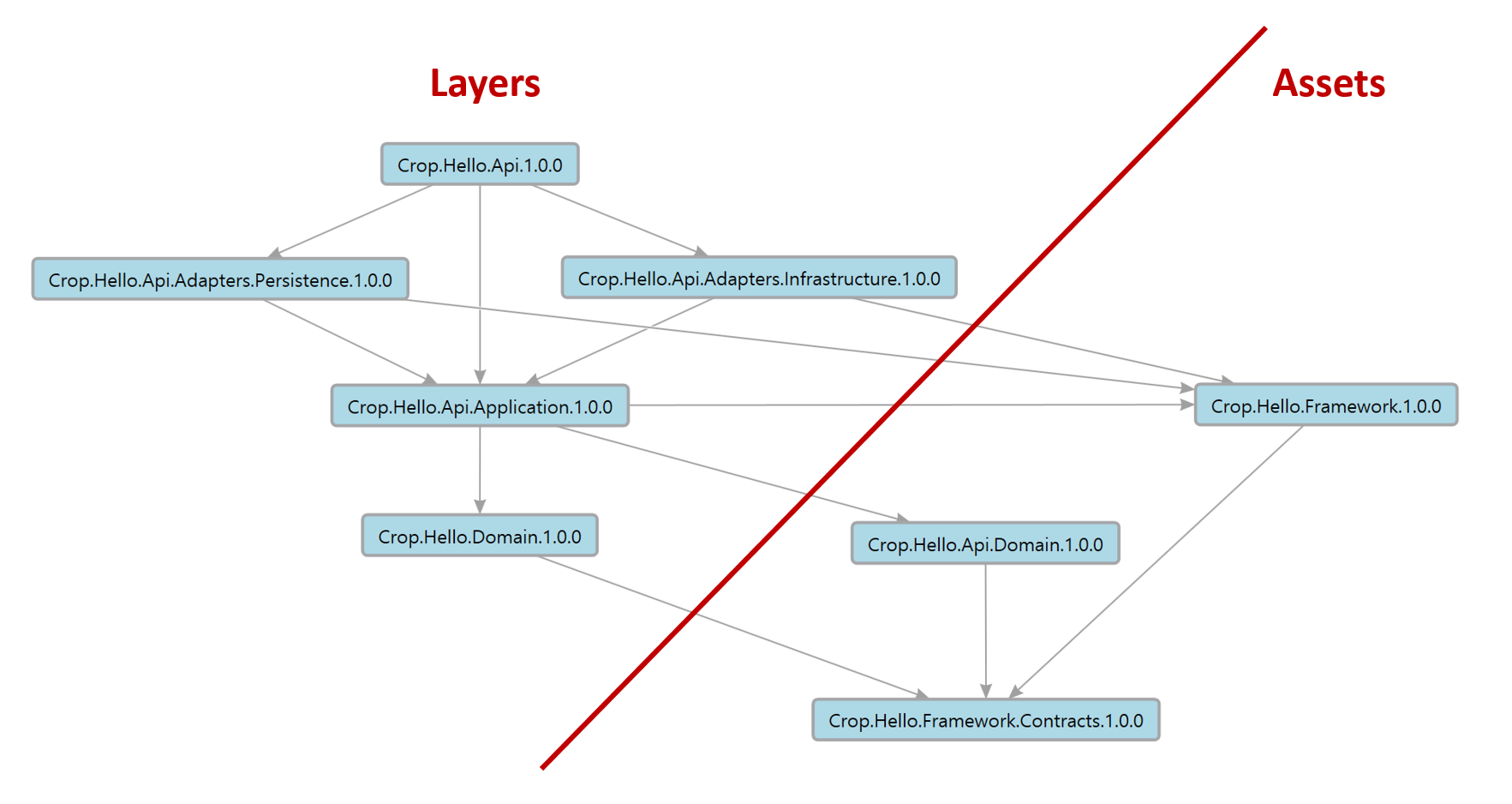
레이어별 주요 목표
주요 목표를 달성하기 위한 모든 부가 활동은
Abstractions폴더에 관련 코드를 배치 시킵니다.
| 구분 | 목표 | 레이어 |
|---|---|---|
| 비즈니스 주요 목표 | 유한 | Domain 레이어(비즈니스 단위), Application 레이어(비즈니스 흐름) |
| 기술 주요 목표 | 무한 | Adapter 레이어 |
- 비즈니스 주요 목표: 유한
- 비즈니스 단위(Domain 레이어): Aggregate Root
- 비즈니스 흐름(Application 레이어어): Use Case
- 기술 주요 목표: 무한
레이어 예제
shell
#
# 비즈니스 단위: Domain 레이어
#
Corp.Hello.Api.Domain
├─Abstractions // 부가 코드: 의존성, ...
│ ├─...
│ └─Registrations // 의존성 등록
│
└─AggregateRoots // 주요 코드: 비즈니스 단위, 유한
├─...
#
# 비즈니스 흐름: Application 레이어
#
Corp.Hello.Api.Application
├─Abstractions // 부가 코드: 의존성, ...
│ ├─...
│ └─Registrations // 의존성 등록
│
└─UseCases // 주요 코드: 비즈니스 흐름, 유한
├─...
#
# 기술: Adapter 레이어
#
Corp.Hello.Api.Adapters.Infrastructure
├─Abstractions // 부가 코드: 의존성, ...
│ ├─...
│ └─Registrations // 의존성 등록
│
├─... // 주요 코드: 기술, 무한
│ ├─...
└─... // 주요 코드: 기술, 무한
├─...Q&A
- Internal 아키텍처를 주관하는 레이어는?
※ 주관 (主管, 어떤 일의 주가 되어 그 일을 책임지고 맡아 관리함)